
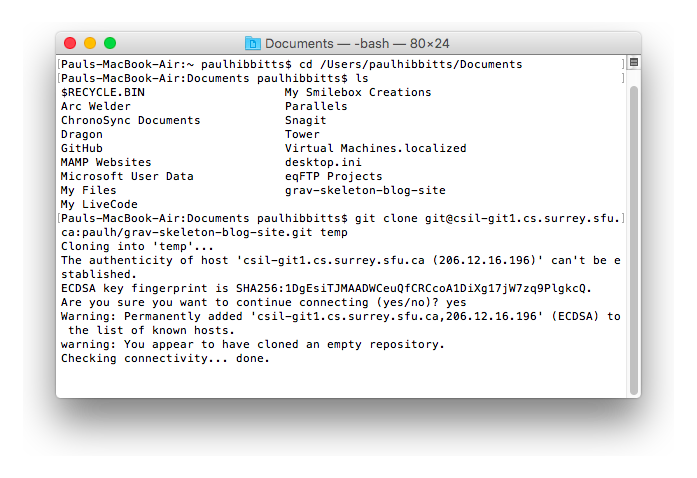
If you're running macOS Sierra 10.12.2 or later, you will need to modify your ~/.ssh/config file to automatically load keys into the ssh-agent and store passphrases in your keychain: Host * Run the following commands to add your SSH key to the ssh-agent. ssh-keygen -t rsa -C # Creates a new ssh key, using the provided email as a label Add your SSH key to the ssh-agent The default settings are preferred, so when you're asked to enter a file in which to save the key, just press Enter to continue. To do that you need to run the commands below, and make sure to substitute the placeholder with your email. If you don't have an SSH key you need to generate one. If you don't have either of those files then read on, otherwise skip the next section. ssh directory, if they existĬheck the directory listing to see if you have files named either id_rsa.pub or id_dsa.pub. Check for existing SSH keysįirst check for existing SSH keys on your computer by running: ls -al ~/.ssh These instructions are for those who wish to use SSH and not HTTPS, and are from the official documentation. Then, configure the remote and push to GitHub by running: git remote add origin If you are setting up a new repo, add at least one file and commit first. Set up a new or existing repo with HTTPS for GitHub If you did not, follow the instructions in the section below.
Clone repositories using HTTPSĪfter creating a new repo on GitHub, clone it using: git clone These instructions are from the official documentation. git config -global credential.helper osxkeychain To prevent git from asking for your username and password every time you push a commit you can cache your credentials by running the following command, as described in the instructions. There are also instructions for using SSH.
#Setup git on mac os code#
To push code to your GitHub repositories, we will use the recommended HTTPS method. Git config -global user.email will get added to your. Next, we'll define your Git user (should be the same name and email you use for GitHub): git config -global user.name "Your Name Here" When done, to test that it installed properly you can run: git -versionĪnd which git should output /usr/local/bin/git.
#Setup git on mac os install#
What's a developer without Git? To install, run: brew install git


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
